Latex
foam rubber consists of a network of open or interconnecting cells,
which may be subjected to large, repeated deformation without damage.
Latex foam is widely used in applications requiring a cool and comfortable
cushioning material, such as pillows.
Manufacturing Process
Batch foaming is suitable for small production units or when miscellaneous
products of varying density and/or colour are required. It is carried
out in a foam mixer consisting of metal bowl and a wire whisk whips
the latex to froth. Control of the volume to which the latex is foamed
is essential and is achieved by marking the frothing bowl or by using
a measure to check the distance of the foam from the top of the bowl
when the whisk is stopped.
The initial foaming is carried out at high speed; when the foam is
approaching the final volume the speed is reduced to a medium rate.
Just before the required volume is reached zinc oxide dispersion (10
parts p.h.r of a 50% dispersion) is added.
Stirring is continued for 45-60 seconds and the speed of the mixer
is again reduced to the slowest rate and the sodium silicoflouride
dispersion (usually 4 - 5 parts p.h.r of a 20% dispersion) is slowly
added.
|
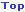
 |
| NR latex Foam Sample |
 |
| Latex Foam Mattress |
 |
|
For high rates of production involving large quantities
of products at a fixed density, continuous foaming equipment, using
a mould conveyor system, is normally used. In a continuous foamer
the latex compound and air are metered under pressure into a foaming
head consisting of a rotor enclosed by two stators. Both rotor and
stators have a large number of protruding lugs with clearances small
enough to provide sufficient shear to foam the latex when the rotor
revolves. The foam passes, via a length of hose, to a blender into
which the dispersions of zinc oxide and gelling agent are metered
and mixed with the foam. From the blender the fully compounded foam
is discharged into moulds again by way of flexible hose.
When the foaming operation is completed the foam
is immediately transferred into two piece mould designed to produce
the desired shape and size of the finished unit. After gelation, the
foam is vulcanised by heating for 20 - 50 minutes at 100°C. After
vulcanisation the mould is opened and wet cured foam is removed and
washed in running water. After the excess water has been removed,
drying may be completed either bath - wise in an oven or tunnel oven.
After drying, the products are trimmed and examined before packing.
Dunlop Process
The process for making latex foam by the Dunlop process can be summarized
as follow:
- Preparation of latex compound
- Foaming of latex - mechanical incorporation of air into a suitable
latex compound
- Addition of a delayed gelling agent
- Time to shape into mould before it gels (depends on the gelling
agent)
- Gelling process in mould
- Vulcanisation on of wet gel
- De-moulding the foam
- Washing and Drying
- Finishing
 |
|
 |
|




