 Natural
rubber latex (NRL) is one of nature's most versatile materials and
the polymer of choice for medical devices. It is a cost-effective
material that provides good barrier properties, durability and comfort.
However, the emergence of latex protein allergy has generated adverse
publicity on the acceptability of NRL in the health care sector
by anti-latex lobby. This has prompted extensive R & D efforts to
reduce the incidence of allergy and ensure that NRL medical gloves
are of minimum health risk.
One of the solutions to address the latex protein allergy is to
use low protein NR latex (LOPROL). This type of latex can be prepared
by treating latex with proteolytic enzyme or a suitable surfactant
and purification process by dilution, centrifugation or membrane
separation. The reaction mechanism for breakdown of polypeptide
chain by enzyme is shown below.
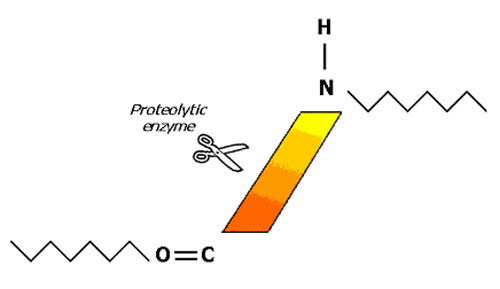
Enzyme Reaction on Protein Molecule
Manufacturing Process
A. Enzyme Treatment
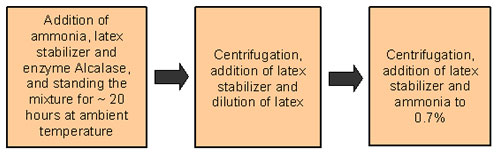
The MRB has developed several processes of producing low protein
NR latices using proteolytic enzymes such as Alcalase or Savinase.
The flowchart below shows one of the processes of producing low
protein NR latex.
 B. Non-enzymatic process
B. Non-enzymatic process
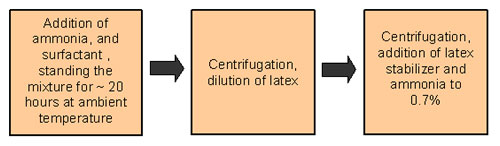
The MRB has also developed several processes of producing low protein
NR lattices using non-enzymatic process. The flowchart below shows
a typical non-enzymatic processes of producing low protein NR latex.
 Properties
Properties
The nitrogen content of low protein latex prepared using enzymatic
and non-enzymatic process is in the range 0.05% - 0.09% and 0.02%
- 0.06% respectively. The extractable protein content of wet-gel
leached plus post dry-leached films prepared from these two type
of latices is less than 100 g/g. The physical properties of sulphur
vulcanised films prepared from these latices are comparable to those
prepared from normal NR latex concentrate.
|




