Paddy has
to be dehusked and polished to convert it into the marketable form
of white rice. In the past, dehusking of the paddy was done manually
by pounding the paddy in a receptacle with a wooden stump. This was
later replaced by mechanical dehusking with the use of rubber rollers,
which gave a greater dehusking efficiency and less grain breakage.
When Malaysia started her factories in the 1970's, the rollers produced
were based on silica-filled styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) compounds
because of their longer service life and better thermal stability
compared to natural rubber (NR) rollers. However, lately many alternative
materials such as acrylonitrile rubber especially the carboxylated
grades, polychloroprene rubbers, EPDM, etc. were being used to give
even longer service life than the SBR rollers.
In a modern rice miller, a pair of rubber-lined
rollers are mounted in an enclosed chamber and driven at a friction
ratio (figure 1). A typical unit using 254 mm nominal width
x 254 mm outer diameter rollers run at 1.28 : 1 friction ratio with
the faster roller at 900 revolutions per minute. The nip of the rollers
is manually adjusted during dehusking to compensate for the gradual
abrasion of the rubber surface and its thermal softening. The paddy
in passing through the rollers nip is subjected to both compressive
and shearing forces. When these forces are correctly predetermined
for a particular grade of paddy (by rubber hardness, resilience, rollers
nip, speed and friction ratio) the paddy will remain substantially
intact after going through, while the husk is broken off. In practice,
the dehusking efficiency can be as high as 90% per pass.
|

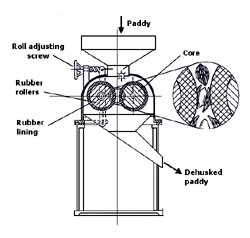
Figure1: Paddy dehusking machine

|
Rice millers are often run between 15 to 24 hours
a day non-stop and causes the roller temperature reaching up to 80°C.
Taking into account the above factors, the compound design of a paddy-dehusking
roller should satisfy the following criteria:
- Low cost
- Easy processing
- Good service life
- Good dehusking efficiency which determined by roller hardness
usually 93±3 IRHD, etc.
- Good final product i.e. white rice
Manufacturing Process
There are a number of possible routes to manufacture
paddy dehusking rollers (see the flow chart). The most establish
process is that of mixing (two-roll mill or internal mixer), pre-warming,
calendaring, laminating to the metal core, preshaping, mould insertion
and autoclave curing. Press moulding is commercially practiced but
the economics of scale appear unfavourable. There are also possible
alternative routes such as the use of wrapped laminated nylon tape
thus dispensing with the use of moulds.
|
|
 |
|




