 Rubber
has for many years been used for sealing purposes in a vehicle. It
is flexible and resilient and can be extruded relatively easily. The
seals for automotive windows, door, light, boot, etc., may all be
considered as weatherstrips or weatherseals. In the early '70s, automotive
weatherstrip was made from a single rubber, mainly natural rubber
which has excellent resilience but relatively poor weathering resistance.
Towards the end of the 70s, EPDM had become dominant primarily because
of its superior weathering and ozone resistance coupled with its high
filler acceptance and wide processing capabilities. Rubber
has for many years been used for sealing purposes in a vehicle. It
is flexible and resilient and can be extruded relatively easily. The
seals for automotive windows, door, light, boot, etc., may all be
considered as weatherstrips or weatherseals. In the early '70s, automotive
weatherstrip was made from a single rubber, mainly natural rubber
which has excellent resilience but relatively poor weathering resistance.
Towards the end of the 70s, EPDM had become dominant primarily because
of its superior weathering and ozone resistance coupled with its high
filler acceptance and wide processing capabilities. |
Manufacturing
process
Modern automotive weatherstrip for door and boot
seals commonly consists of solid or co-extruded solid and cellular
profiles whilst window seal profiles can contain a metal insert for
added stiffness or be multiple co-extrusions of different hardness
compounds. Rapid curing of the extruded profile is achieved at high
temperature by a continuous vulcanisation procedure such as microwave,
liquid curing medium (LCM) or the fluidised bed (Ballotini) method.
- Preparation of rubber compound
In choosing a compound for use as weatherstrip, a number of considerations
have to be made. In its uncured state, the extruded profile must
possess high green strength to prevent collapse and so maintain
its correct shape. The surface finish of the extruded profile must
also be very good. Mixing of the rubber compound can be carried
out on a two-roll mill or in an internal mixer. In the case of an
internal mixer, it can be done in a single-stage or a double-stage
mixing. Curatives are normally added on a two roll mill.
- Determination of scorch time, cure characteristics
and physical testing (e.g., hardness, tensile properties, tear
resistance, rebound resilience, compression set, flex-cracking
resistant and ozone resistance).
The above properties are necessary before the compounds can proceed
to the subsequent fabrication process such as extrusion.
|
|

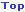
Door Outer

Tail gate/trunk lid

Door opening inner

Hood
|
- Fabrication and curing of the weatherstrip
The profiles are extruded and good surface finish appearance is
required especially if the product is used in a highly visible part
of a car where aesthetic appearance is highly important. Curing
is normally carried out continuously using microwave, LCM or Ballotini.
A single extruder or a combination of extruders are commonly used
to produce weatherstrip, depending on whether the product is of
one solid profile, co-extruded solid and cellular profiles or one
that contains two or more solid profiles of different hardnesses.
- Jointing
The extruded profile is then transferred to the jointing presses
whereby the cut pieces are joined together by the presses into its
finished form.
- Assembly on the vehicle
 |




